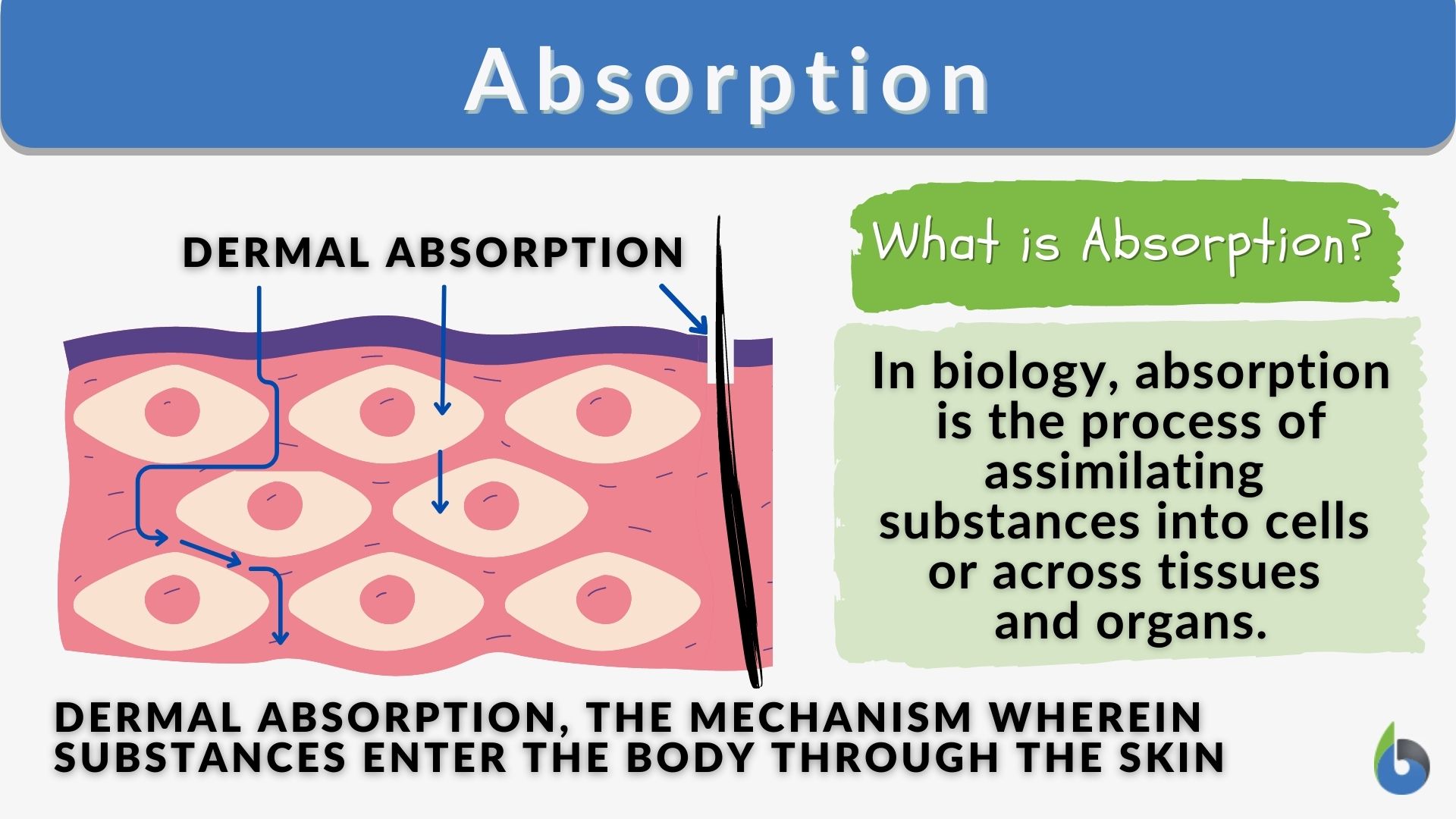
What Absorbs Blood . the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. It consists of the heart and. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. Most of these travel in the. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis.
from www.biologyonline.com
blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. Most of these travel in the. It consists of the heart and. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract.
Absorption Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
What Absorbs Blood identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. It consists of the heart and. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. Most of these travel in the.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Metabolic States of the Body Anatomy and Physiology II What Absorbs Blood nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. It consists of the heart and. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Pulse Oximetry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5329456 What Absorbs Blood nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. Most of these travel. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.biologyonline.com
Absorption Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary What Absorbs Blood Other functions include supplying oxygen and. Most of these travel in the. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. It consists of the heart and. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.bbc.co.uk
BBC Radio 4 Radio 4 in Four Thirteen blood facts to absorb What Absorbs Blood blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. It consists of the heart and. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. the blood circulatory system. What Absorbs Blood.
From openoregon.pressbooks.pub
The Digestive System Nutrition Science and Everyday Application What Absorbs Blood Most of these travel in the. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. It consists of the heart and. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.differencebetween.com
What is the Difference Between Fat Soluble and Water Soluble Statins Compare the Difference What Absorbs Blood Other functions include supplying oxygen and. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. It consists of the heart and. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.fiercebiotech.com
FDA approves Abbott's Absorb, the first completely resorbable heart stent FierceBiotech What Absorbs Blood the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. It consists of the heart and. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.visiblebody.com
Functions of the Blood Circulatory Anatomy What Absorbs Blood blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. It consists of the heart and. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.researchgate.net
Top (From Left) (i) Blood sample of 1mL of blood is poured on khadi... Download Scientific Diagram What Absorbs Blood It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of. It consists of the heart and. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. Most of these travel in the. Other functions include supplying oxygen and.. What Absorbs Blood.
From teachmephysiology.com
Absorption in the Large Intestine Regulation TeachMePhysiology What Absorbs Blood blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. Most of these travel in the. It helps to maintain homeostasis through the release or conservation of.. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.visiblebody.com
Functions of the Blood Circulatory Anatomy What Absorbs Blood blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. Most of these travel in the. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of. What Absorbs Blood.
From philschatz.com
Tubular Reabsorption · Anatomy and Physiology What Absorbs Blood Most of these travel in the. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.pinterest.ca
GI absorption of nutrients Physiology, Nursing tips, Anatomy and physiology What Absorbs Blood It consists of the heart and. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.tasnimnews.com
Surprise Finding Blood Clots Absorb Bacterial Toxin Science news Tasnim News Agency What Absorbs Blood blood performs many functions critical for sustaining metabolic physiological processes in complex organisms. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. the blood circulatory system. What Absorbs Blood.
From avantesusa.com
Buckets of Blood Absorbance Spectra Comparison with Fake Blood Avantes What Absorbs Blood identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. It helps to maintain homeostasis through. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.nagwa.com
Question Video Describing the Function of the Lacteals in the Small Intestine Nagwa What Absorbs Blood It consists of the heart and. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. Most of these travel in the. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds. What Absorbs Blood.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Chemical Digestion and Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy and Physiology II What Absorbs Blood the blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. It consists of the heart and. identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. blood plays an important role in regulating the body’s systems and maintaining homeostasis. the carbon. What Absorbs Blood.
From www.pinterest.com
Glucose is absorbed in the small intestine by a secondary active transport mechanism down t What Absorbs Blood identify the primary functions of blood in transportation, defense, and maintenance of homeostasis. the carbon dioxide is absorbed from the cells by the blood plasma (some of it binds to hemoglobin too) and is transported back to the. Other functions include supplying oxygen and. blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. Most of these travel in. What Absorbs Blood.